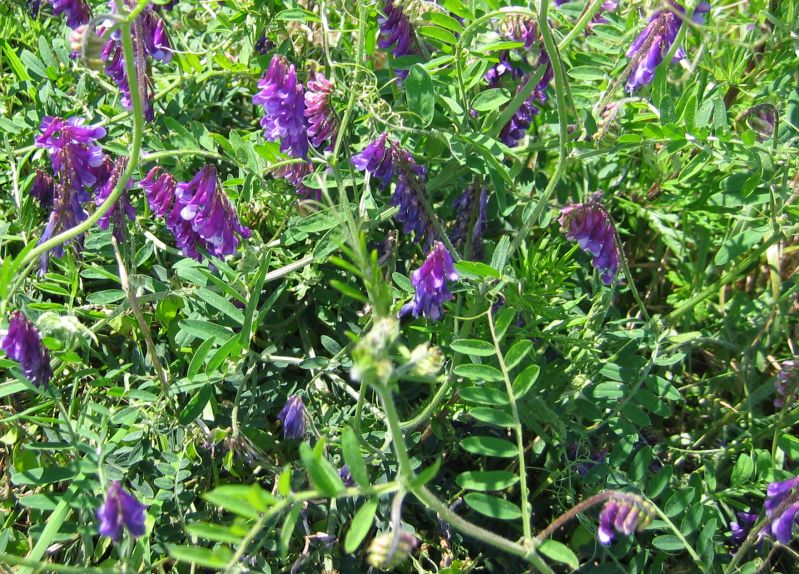
HAIRY VETCH
Summary
Hairy vetch is a hardy type of vetch suited to wetter soil and colder winters than other winter-active legumes. Hairy vetch develops best under cool temperature conditions on fertile loam soils; it is also productive on sandy or clay soils. It has been reported to grow well on light soils that are too sandy for crimson clover. It is only moderately sensitive to soil acidity.
Plant Characteristics
Taxonomy
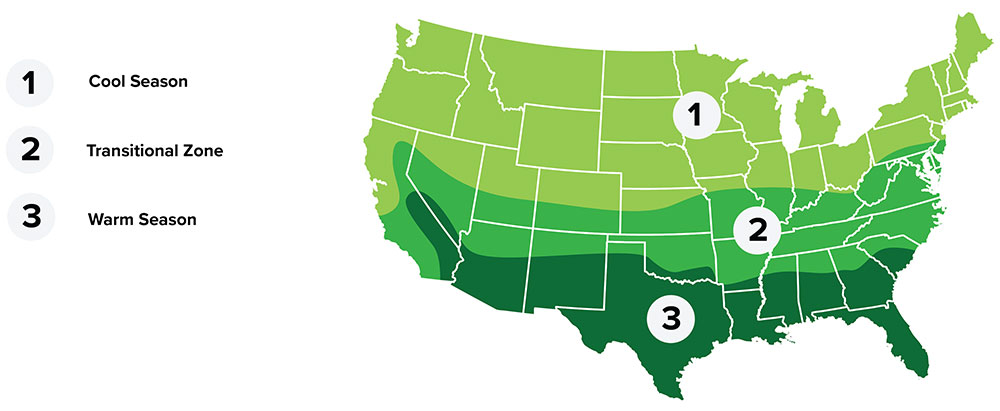
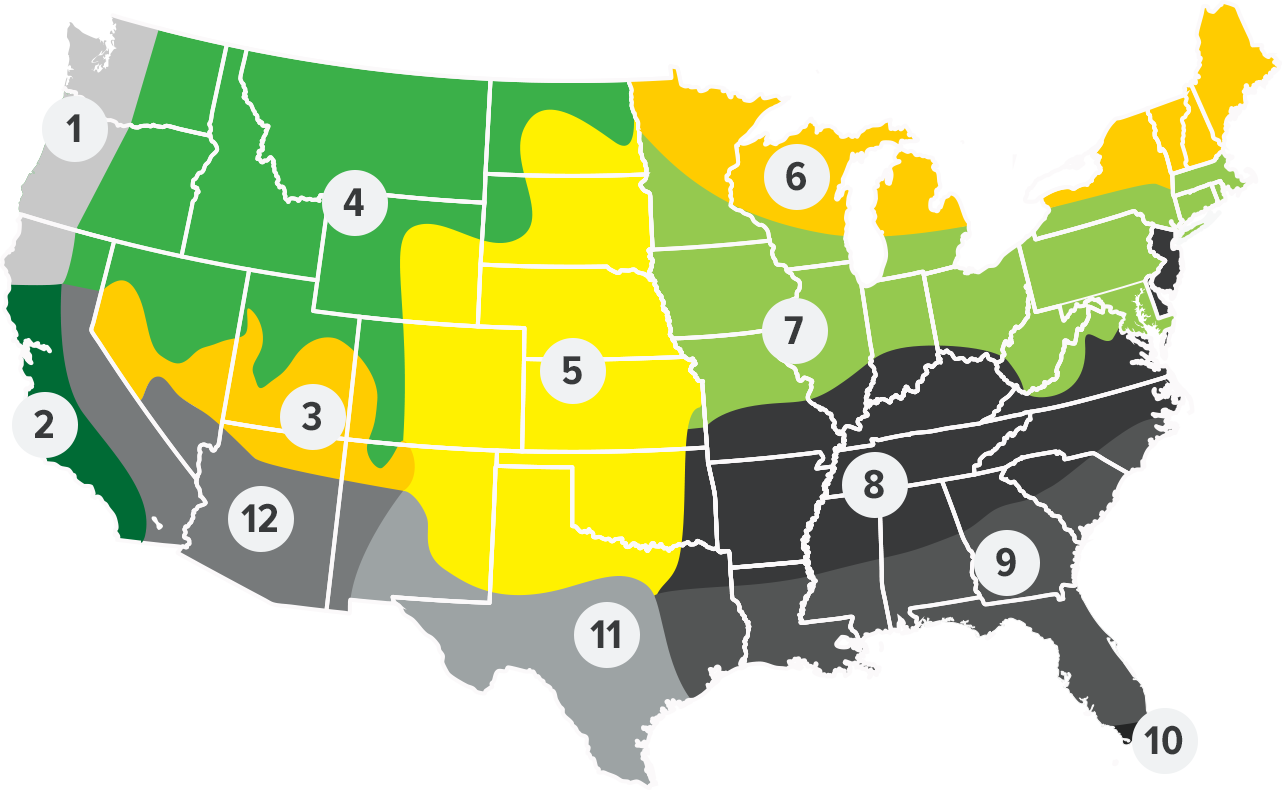
Zone
- Regional Growing Zone
- 1 - Northwest Coastal, 2 - California Coastal, 3 - Southern Mountain, 4 - Mountain, 5 - Midwest, 6 - Northeast Lakes, 7 - Great Lakes South, 8 - Appalacia, 9 - Southeast, 10 - South Florida
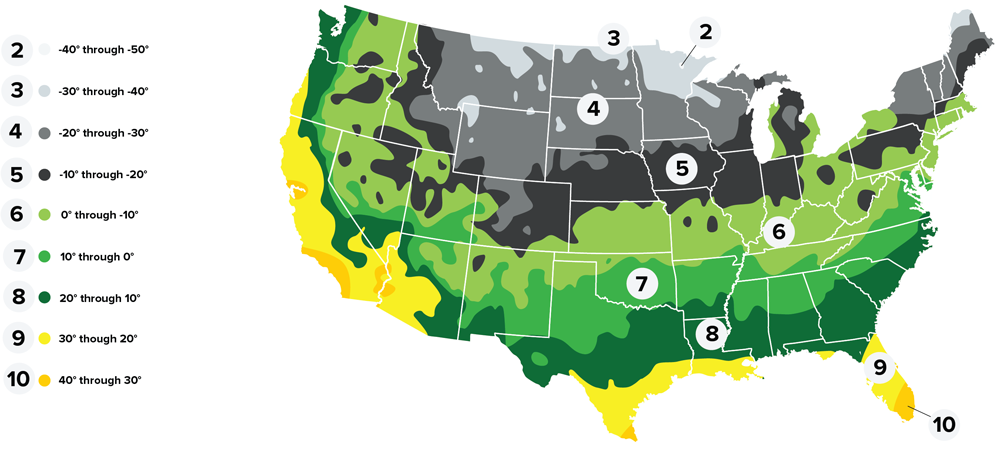
- USDA Plant Hardiness Zones
- 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
- Temperature Zone
- Warm, Cool, Transitional
Plant Characteristics
- Height
- 24" - 48"
- Bloom Period
- Early-Spring
- Bloom Color
- Purple
- Leaf Color
- Green
- Growing Cycle
- Annual
- Growth Habit
- Other
- Sun Requirement
- Full Sun
Plant Information
- Planting Season
- Fall
- Plant Depth
- 1.5" - 2"
- Minimum Soil Temp for Germination
- 48° F
- Establishment
- Easy
Seed Information
- Seeds Per Pound
- 16,000
- Kingdom
- PLANTAE
- Subkingdom
- TRACHEOBIONTA
- Super Division
- SPERMATOPHYTA
- Division
- MAGNOLIOPHYTA
- Class
- MAGNOLIOPSIDA
- Subclass
- ROSIDAE
- Order
- FABALES
- Family
- FABACEAE
- Genus
- VICIA
- Species
- VICIA VILLOSA
Coverage Area & Available Sizes
How to Use & Apply
Hairy vetch is planted in the fall wherever it is grown. It is normally seeded at 20 to 40 pounds per acre. Due to the vining, climbing habit of the plant, it is often sown in combination with rye so the rye may provide some support.
Applications
Hairy vetch’s capacity to provide a heavy mulch aids in soil and water conservation.
Hairy vetch is noted for its ability to fix large quantities of nitrogen.
It is grown for hay, pasture, silage, seed, or as interim cover on disturbed soil.
Notes
Don’t forget to purchase the required inoculant for this product.